The Refugee Crisis: Challenges and Solutions
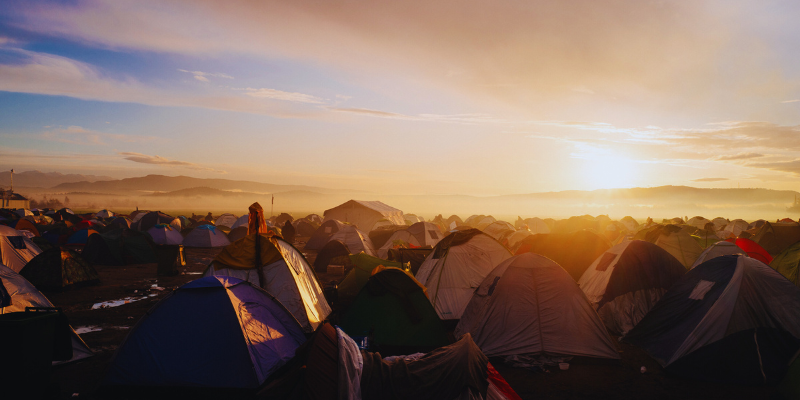
The refugee crisis is one of the most pressing humanitarian challenges of our time. It is characterized by the mass displacement of millions of people who flee their homes due to conflict, persecution, violence, and human rights abuses. As the number of refugees worldwide continues to grow, it is essential to understand the complex challenges they face and explore sustainable solutions to address this global crisis. In this blog, we will delve into the challenges posed by the refugee crisis and examine potential solutions to mitigate its impact and support those affected.
Understanding the Refugee Crisis
The refugee crisis is a global phenomenon that affects millions of individuals and families across the globe. According to the United Nations Refugee Agency (UNHCR), there are currently over 26 million refugees worldwide, half of whom are under the age of 18. These refugees are forced to flee their homes in search of safety, security, and protection from persecution, violence, and conflict.
The refugee crisis is fueled by various factors, including armed conflict, political instability, human rights abuses, environmental disasters, and economic hardship. Wars and conflicts in countries such as Syria, Afghanistan, South Sudan, and Myanmar have contributed to the mass displacement of millions of people, leading to a protracted and complex humanitarian crisis.
Challenges of the Refugee Crisis
1. Humanitarian Needs
The influx of refugees places immense strain on humanitarian organizations and host countries, which struggle to meet the basic needs of displaced populations. Access to essential services such as food, clean water, shelter, healthcare, and education is often limited in refugee camps and host communities, leaving refugees vulnerable to malnutrition, disease, and exploitation.
2. Protection and Security
Refugees face significant protection risks, including violence, exploitation, discrimination, and human trafficking. Many refugees are forced to embark on perilous journeys, often crossing dangerous borders, seas, and landscapes in search of safety and protection. Women, children, and marginalized groups are particularly vulnerable to violence, abuse, and exploitation, both during their journey and in refugee camps.
3. Legal and Policy Challenges
Refugees often encounter legal and policy barriers that restrict their access to asylum, protection, and basic rights in host countries. Many countries have restrictive immigration policies, lengthy asylum procedures, and limited resettlement opportunities, leaving refugees in protracted displacement and legal limbo. The lack of legal status and documentation further exacerbates refugees’ vulnerability and limits their access to essential services and rights.
4. Social and Economic Integration
Refugees face numerous challenges in integrating into host communities and rebuilding their lives in a new environment. Language barriers, cultural differences, and limited access to education and employment opportunities hinder refugees’ social and economic integration, perpetuating cycles of poverty, marginalization, and social exclusion. Negative attitudes, xenophobia, and discrimination towards refugees also pose significant obstacles to their successful integration and acceptance in host societies.
Solutions to the Refugee Crisis
1. Addressing Root Causes
To effectively address the refugee crisis, it is essential to tackle the root causes of displacement, including conflict, persecution, poverty, and environmental degradation. International efforts to prevent and resolve conflicts, promote peacebuilding and reconciliation, and address the underlying drivers of displacement are critical to preventing further mass displacement and protecting the rights and safety of vulnerable populations.
2. Strengthening Refugee Protection
Enhancing refugee protection and upholding the rights and dignity of displaced populations are paramount to addressing the refugee crisis. This includes ensuring access to asylum, protection from violence and exploitation, and safeguarding the rights of refugees under international law. Governments must commit to the principles of refugee protection, including the right to seek asylum, non-refoulement, and the principle of family unity, and provide adequate legal frameworks and resources to protect and support refugees.
3. Providing Humanitarian Assistance
Humanitarian assistance plays a crucial role in meeting the immediate and long-term needs of refugees and displaced populations. International humanitarian organizations, governments, and civil society actors must work together to provide lifesaving aid, including food, shelter, healthcare, clean water, and education, to refugees in crisis-affected areas and host communities. Timely and coordinated humanitarian responses are essential to addressing the acute needs of refugees and mitigating the impact of the crisis on vulnerable populations.
4. Promoting Education and Empowerment
Education is a fundamental human right and a powerful tool for empowering refugees and building resilience in crisis-affected communities. Investing in quality education and skills training for refugee children and youth can help break the cycle of poverty and dependency, promote social inclusion and cohesion, and equip refugees with the knowledge, skills, and opportunities they need to rebuild their lives and contribute to the development of their communities.
5. Fostering Social and Economic Integration
Promoting the social and economic integration of refugees into host communities is essential for their long-term well-being and self-reliance. Governments, civil society organizations, and local communities should implement policies and programs that facilitate refugees’ access to education, employment, healthcare, housing, and social services, while fostering social cohesion, mutual understanding, and solidarity between refugees and host populations.
6. Strengthening International Cooperation
Addressing the refugee crisis requires a coordinated and collaborative approach involving governments, international organizations, civil society, and the private sector. Strengthening international cooperation and solidarity is essential to mobilizing resources, sharing responsibilities, and finding sustainable solutions to the refugee crisis. This includes enhancing global refugee protection mechanisms, increasing humanitarian funding, and supporting host countries that bear the brunt of refugee influxes.